The


evolution

———
of
EFTPOS

payments
The evolution









of EFTPOS
payments











1860
Department stores issue charge coins and cards.
In the late 19th century, department stores began offering their customers small ID tags to allow them to purchase goods on credit. These tags (which initially came in the form of coins, before celluloid, copper, and aluminium cards became the norm) were embossed with customer information and placed in an imprinter – arguably the very first payment machine – to create a carbon copy of the details.
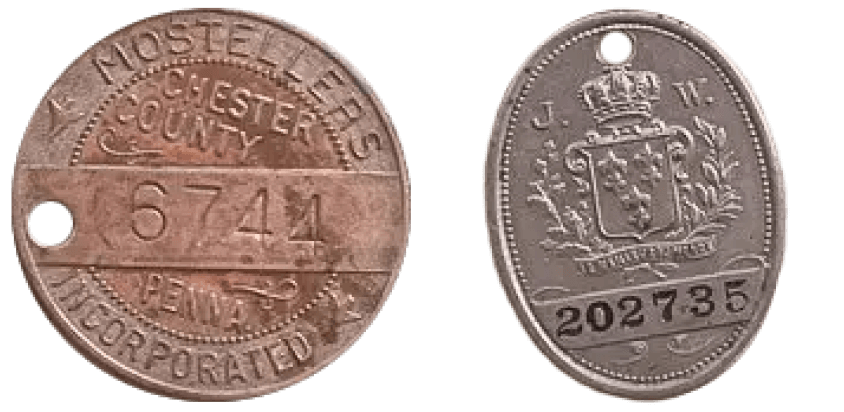 Original charge coins,
Source
Original charge coins,
Source
1946
General purpose charge cards gain popularity.
In 1946, John Biggins of the Flatbush National Bank of Brooklyn introduced Charg-It, the first bank-issued card, however it could only be used within a two-block radius of his bank. Four years later, Frank McNamara and Ralph Schneider founded Diners Club International, enabling customers to use their charge cards at different branches and companies across a broad geography.
 Diners’ Club Card,
Source
Diners’ Club Card,
Source
1958
The first credit cards enter circulation.
In 1958, American Express introduced its first charge card while in the same year, Bank of America introduced the BankAmericard (later renamed Visa) the first card with a revolving credit system. Barclays followed suit, launching the UK’s first all-purpose credit card in 1966. By the end of the 20th century, credit cards – as well as debit cards, and alternative forms of cashless payments – became widely adopted globally.
 BankAmericard,
Source
BankAmericard,
Source
1960
The ‘click-clack’ machine makes its entry.
Early payment cards were made of cardboard and required manual recording at the point of sale. In 1959, American Express introduced the first plastic credit card, featuring embossed lettering for the cardholder's details. This innovation allowed merchants to use a credit card imprinter, also known as a "click-clack" machine, to create imprints on carbon paper slips for proof of purchase.
 Early credit card imprinter from circa 1960,
Source
Early credit card imprinter from circa 1960,
Source
1970
Magstripe enables electronic payment terminals.
In 1970, payment cards gained electronic capabilities with the addition of a magnetic stripe, which stored the cardholder's details. Electronic payment terminals were developed to read these cards, enabling secure transactions and real-time account balance checks, however widespread use of electronic terminals connected to Visa and Mastercard networks didn’t arrive until the 1980s.
 The first Magnetic Stripe plastic credit card,
Source
The first Magnetic Stripe plastic credit card,
Source
1979
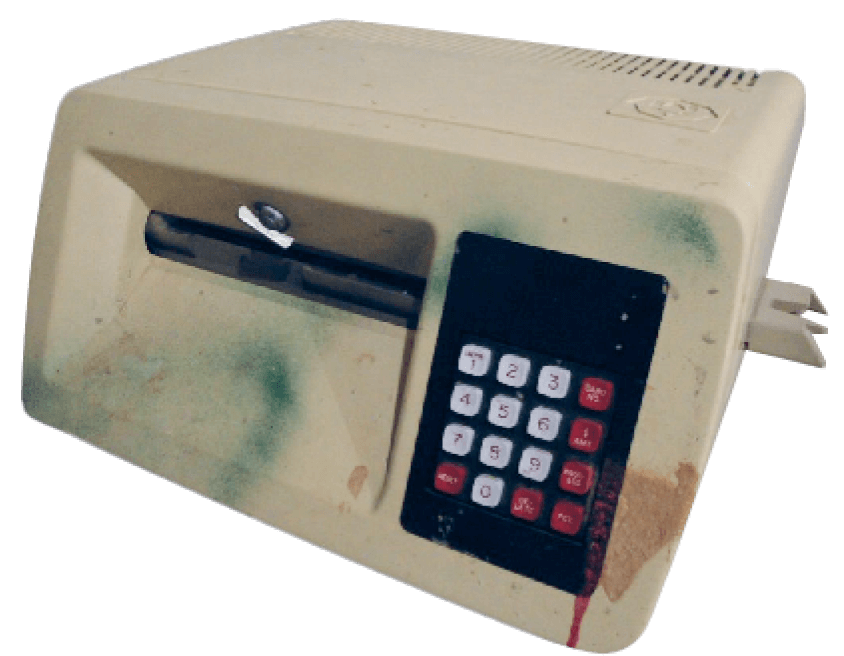
The advent of the electronic card terminal.
National BankAmericard introduced the first electronic system for authorising, clearing, and settling funds in 1973, however it still required a 5-minute phone call per transaction. It wasn’t until 1979 when Visa launched its bulky electronic card machines that the technology really took a step forward. This marked MasterCharge's rebranding to MasterCard and credit cards were replaced to include a magnetic stripe.
 Visa’s 1979 card machine,
Source
Visa’s 1979 card machine,
Source
1982
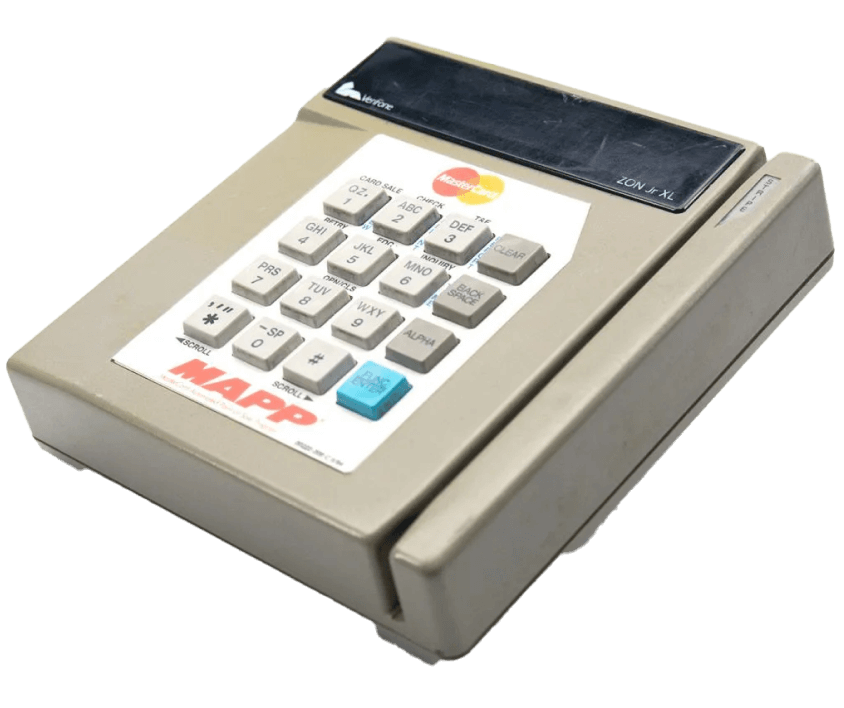
Electronic funds transfer at point of sale (EFTPOS) is born.
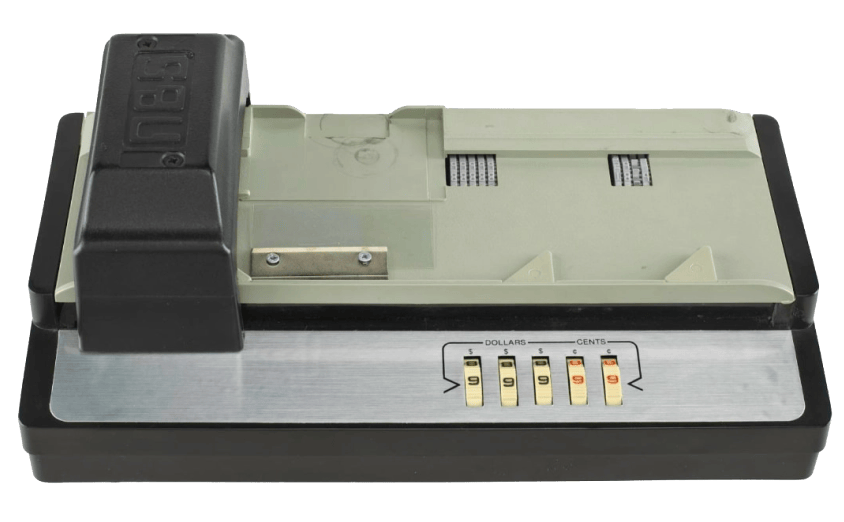
One of the first companies to produce dedicated payment terminals was Verifone. This small Hawaiian electronics company released their first POS terminal in 1982, which became the benchmark model. These machines required a landline connection and had to be fixed and connected via cable to a telephone socket. In Australia, Westpac and Woolworths were the first companies to trial the EFTPOS system.
 Verifone ZON JR XL 1984,
Source
Verifone ZON JR XL 1984,
Source
1996
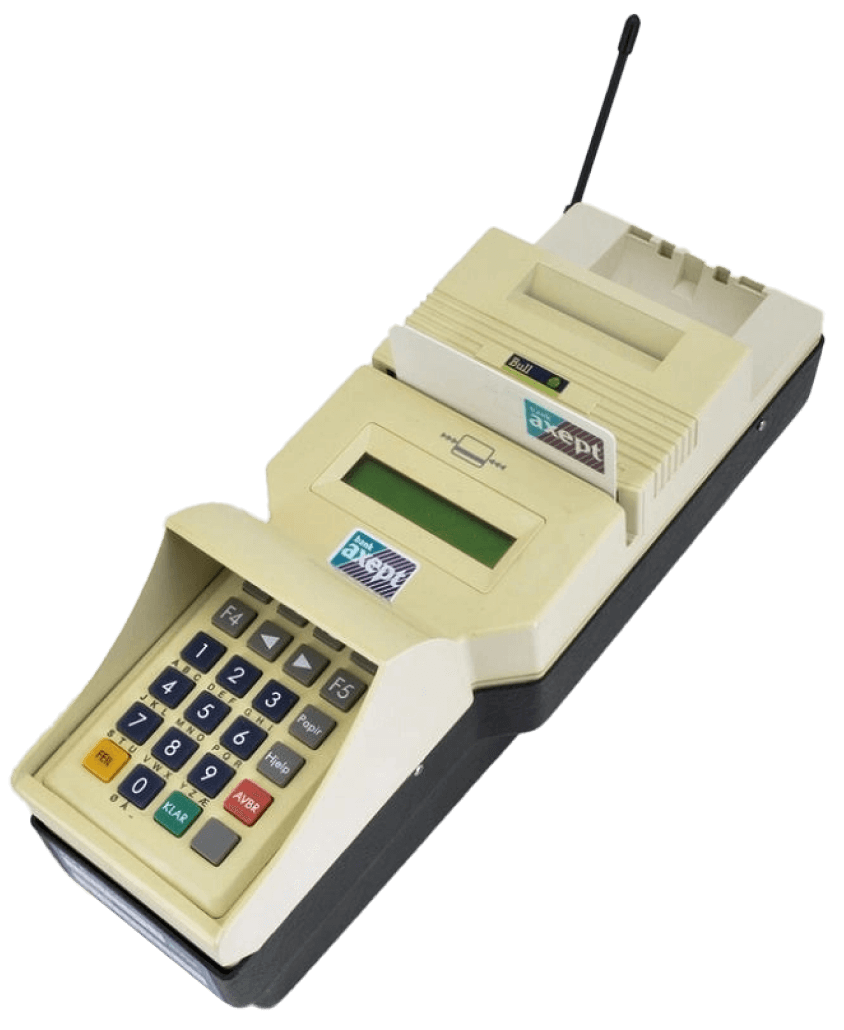
EFTPOS goes mobile with the internet.
With the internet came the development of wireless technology, which allowed businesses to process payments anywhere using portable devices connected via cellular networks or Wi-Fi. These terminals provided greater flexibility for merchants and by 2004, cellular-based EFTPOS infrastructure had rapidly expanded. By 2010, it had become the global market standard.
 Norwegian Telenor Mobile’s wireless card terminal 1997,
Source
Norwegian Telenor Mobile’s wireless card terminal 1997,
Source
2000
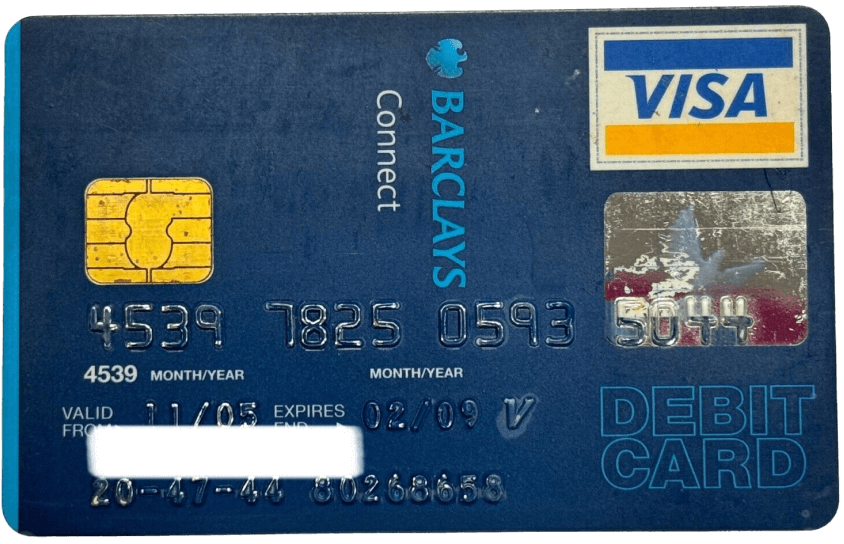
Chip and PIN technology brings greater security to payments.
The patented chip card (which was originally invented in France in 1975 for calling cards) was eventually adopted on bank cards in 1985, but didn’t become widely adopted until many countries mandated it in the early 2000s as a way to combat fraud. Compared to the magnetic stripe, whose information could be easily cloned, chip technology generates unique transaction data for each use, making them significantly more secure against scammers.
 Barclays Connect Visa Debit Card with chip technology 2005,
Source
Barclays Connect Visa Debit Card with chip technology 2005,
Source
2004
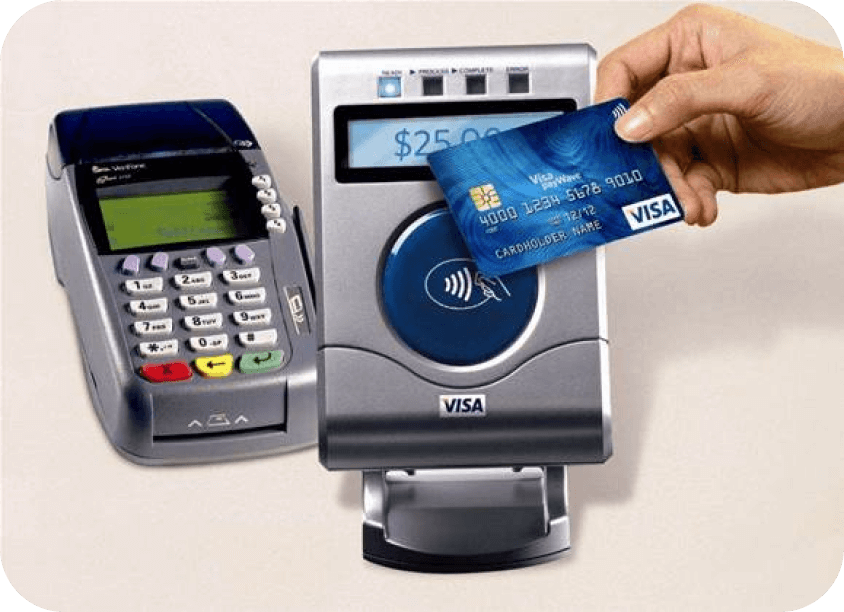
NFC technology enables contactless payments.
In 2004, near field communication (NFC) technology was greatly enhanced thanks to Nokia, Sony, and Philips who came together to form the NFC Forum. This technology allowed for data to be exchanged between a payment card and a terminal, simply by tapping the card onto the reader. EFTPOS machines were developed in line with this technology, enabling customers to make small purchases quickly without the need to insert their card or enter a PIN.
 Ingenico-Westpac terminals 2010,
Source
Ingenico-Westpac terminals 2010,
Source
2010s
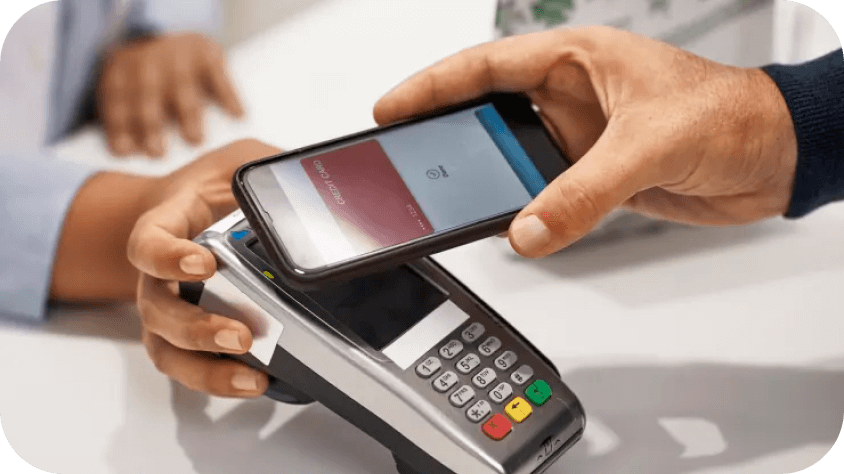
Google, Apple, and Samsung lead the way with digital wallets.
The rise of smartphones and mobile wallet apps marked a significant shift in payment terminal evolution. Platforms such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay enabled secure, contactless transactions via mobile devices. To accommodate these advancements, payment terminals underwent adaptations to integrate seamlessly with diverse mobile wallet platforms. The launch of these mobile wallets also coincided with a wider adoption of card payments generally in Australia, and a shift away from cash.
 Apple Pay contactless transaction,
Source
Apple Pay contactless transaction,
Source
2022
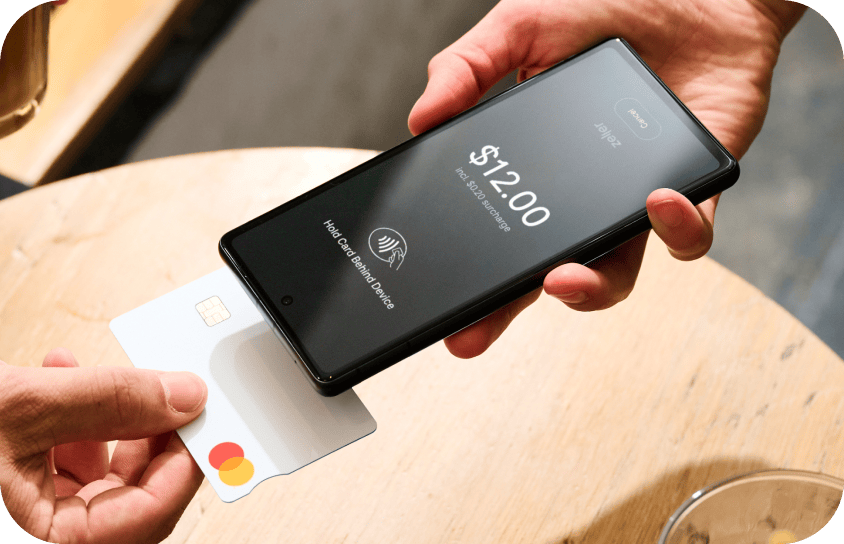
Tap to Pay revolutionises mobile payments.
In 2022, financial institutions such as Zeller, Square, and Stripe, marked a significant shift in payment technology, enabling businesses to accept contactless payments directly on their smartphone – doing away with a traditional EFTPOS terminal altogether. This new solution, known as Tap to Pay, leverages the same NFC technology that is used for making payments with a mobile wallet.
 Zeller’s Tap to Pay on Android 2023,
Source
Zeller’s Tap to Pay on Android 2023,
Source
The
Future
The next generation of EFTPOS machines.
EFTPOS terminals have historically played catch-up with the ever-evolving card technology, however today, their innovation is outpacing its users. New functionalities are being inbuilt into EFTPOS machines to help merchants collect payments faster and provide customer service beyond what has traditionally been expected (bill splitting, tipping, digital receipts, screensavers, and more). Additionally, with the integration of AI and biometric technology, more advanced fraud detection measures are constantly being added. As such, we can expect the next generation of EFTPOS machines to be more seamless and secure than ever.
 Zeller Terminal 2024,
Source
Zeller Terminal 2024,
Source
Copyright 2024